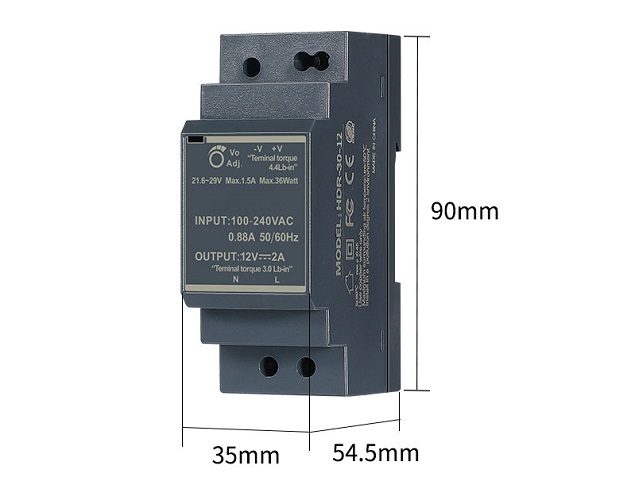
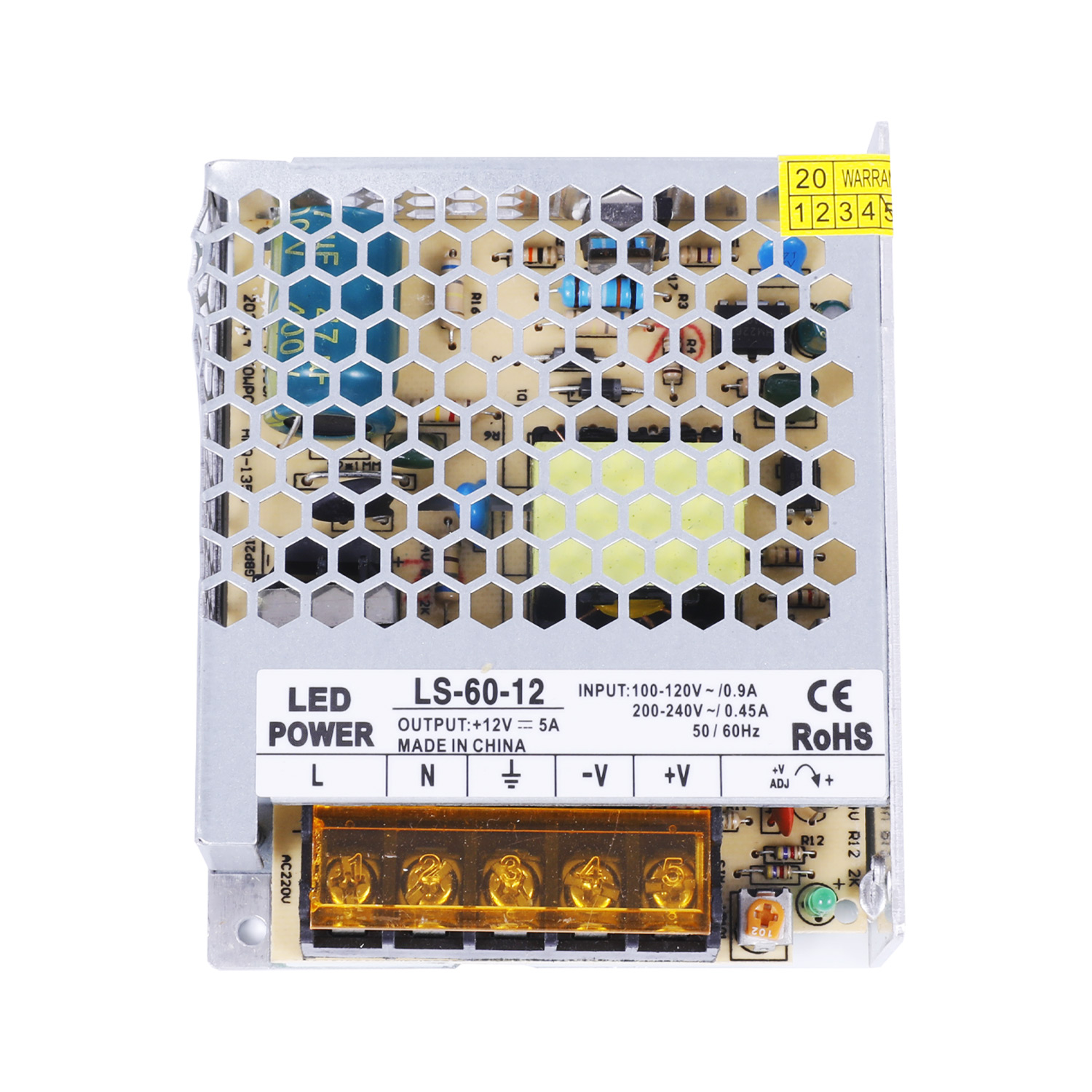
What is the difference between din rail power supply and switching power supply?
Both din rail power supply and switching power supply are power conversion devices, but they are very different in design, performance and use.
The din rail power supply converts the input alternating current into the direct current with reduced depth through circuits such as rectification, filtering and voltage regulation.
Switching power supply uses high-frequency transformer for power conversion, which has higher energy efficiency and power density.
In the selection, the maximum output current of din rail power is generally small, only suitable for PLC, sensor, controller power supply.
Switching power supplies can support a wider range of loads, including computer equipment, communication equipment, industrial automation equipment, etc.
Din rail switching power supply can generally be used in the following scenarios:
building automation , home control systems, industrial control systems, factory automation, mechanical and electrical equipment, machine vision inspection systems , plant cultivation applications, security system applications.
There are many application scenarios, of course, there is still a lot of room for more comprehensive applications of Din rail power supply in the future.
What should pay attention to when choosing din rail power supply?
1) Select the appropriate input voltage specification;
2) Choose the right power supply. In order to make the life of the power supply grow, a model with more than 30% of the rated output power can be selected;
3) Consider the load characteristics. If the load is a motor, lighting or capacitive load, when the starting current is large, the appropriate power should be selected to avoid overload. If the load is the motor should be considered to stop when the voltage is invaded;
4) In addition to the need to consider the temperature of the working environment of the power supply, and there is no additional auxiliary cooling equipment, in the high temperature of the loop power supply to reduce the output;
5) Select various functions according to the needs of the application:
Protection functions: over voltage protection (OVP), over temperature protection (OTP), overload protection (OLP), etc;
Application function: signal function (normal power supply, power failure), remote control, telemetry, parallel function;
Features: Power factor correction (PFC), uninterruptible power supply (UPS);
6) Select the required compliance and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) certification.

 Products
Products News
News